10 lý do cấm thiết bị công nghệ với trẻ em dưới 12 tuổi
Nên cấm thiết bị công nghệ từ điện thoại di động, máy tính bảng, ipad… với tất cả trẻ em dưới 12 tuổi, bởi chúng hạn chế sự phát triển não bộ, là nguyên nhân trẻ em chậm phát triển, béo phì, gây hấn và gia tăng các chứng bệnh tinh thần.
Là một nhà trị liệu cho trẻ, tôi kêu gọi mọi phụ huynh, giáo viên và các chính phủ hãy cấm thiết bị công nghệ đối với trẻ em dưới 12 tuổi.
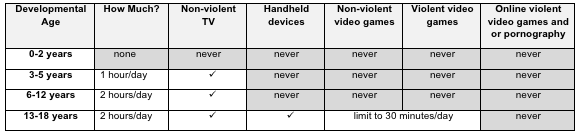
Viện Nghiên cứu Y khoa trẻ em Mỹ và Hội Y khoa Canada tuyên bố rằng, trẻ em từ 0 đến 2 tuổi không nên dính líu gì đến các sản phẩm công nghệ, trẻ em từ 3 đến 5 tuổi cần hạn chế 1 giờ/ngày và trẻ từ 6 đến 18 tuổi hạn chế 2 giờ/ngày.
Trẻ sử dụng thiết bị công nghệ trong khoảng thời gian gấp 4 đến 5 lần so với trên đây sẽ có những hậu quả nghiêm trọng. Các thiết bị cầm tay (điện thoại di động, trò chơi điện tử, ipad) làm gia tăng một cách nghiêm trọng thói quen và tác động của việc sử dụng công nghệ, đặc biệt với thanh thiếu niên.

Dưới đây là 10 nguyên nhân nên cấm tất cả các thiết bị công nghệ với trẻ em dưới 12 tuổi:
1. Kích thích sự phát triển của não bộ
Từ 0 đến 2 tuổi, não của trẻ phát triển gấp 3 lần về kích cỡ, và tiếp tục phát triển nhanh chóng cho đến 21 tuổi. Sự phét triển sớm não bộ của trẻ được quy định bởi những kích thích môi trường.
Sự kích thích đối với sự phát triển của não bộ đến từ việc không kiếm soát các thiết bị công nghệ (điện thoại di động, internet, iPad, ti vi) được cho thấy là có liên quan đến những rối loạn về chú ý và chức năng , sự chậm trễ về nhận thức cũng như suy yếu khả năng học tập, sự gia tăng của tính bốc động và việc suy giảm khả năng tự điều chỉnh.
2. Chậm phát triển
Các thiết bị công nghệ đòi hỏi những vận động hạn chế, điều này là nguyên nhân của chậm phát triển. Cứ một trong ba trẻ độ tuổi đến trường hiện nay bị chậm phát triển trong khả năng đọc viết cũng như các khả năng học tập khác. Sự vận động làm tăng cao khả năng chú ý và học tập. Việc sử dụng thiết bị công nghệ dưới 12 tuổi là không có lợi cho sự phát triển và học tập của trẻ.
3. Bệnh béo phì
TV và trò chơi điện tử có liên quan đến sự gia tăng bệnh béo phì. Trẻ con được phép chơi một thiết bị trong phòng ngủ uarmifnh sẽ có 30% nguy cơ béo phì. Cứ một trong 4 trẻ ở Canada và một trong ba trẻ ở Mỹ bị béo phì. 30% trẻ béo phì có nguy cơ bị đái tháo đường, và những người béo phì có nguy cơ cao bị tim mạch và đột quỵ sớm.
4. Mất ngủ
60% phụ huynh không giám sát việc sử dụng thiết bị điện tử của con, và 75 % trẻ được cho phép chơi thiết bị điện tử trong phòng ngủ. 75% trẻ độ tuổi 9 và 10 bị mất ngủ dẫn tới việc học bị ảnh hưởng rất lớn.

5. Các chứng bệnh về tinh thần
Việc lạm dụng các thiết bị công nghệ là mọt nhân tố làm gia tăng số trẻ em bị trầm cảm, lo lắng, rối loạn gắn bó, có vấn đề về hành vi v.v. Cứ một trong 6 trẻ em Canada bị chẩn đoán có vấn đề về tâm lý, và nhiều trong số đó có nguy cơ phải dùng thuốc trị liệu.
6. Sự gây hấn
Các nội dung bạo lực có thể gây nên sự rối loạn về tinh thần ở trẻ. Trẻ nhỏ ngày càng phải đối mặt với sự gia tăng về bạo lực thể chất và tình dục đầy rẫy trên các phương tiện truyền thông, đặc biệt trong các bộ phim phát trên ti vi
7. Chứng mất trí nhớ kỹ thuật số
Những nội dung trên các phương tiện truyền thông với tốc độ cao có thể gây nên sự suy giảm chú ý cũng như làm giảm khả năng chú ý và trí nhớ, gây ảnh hưởng đến khả năng học tập của trẻ.
8. Nghiện ngập (game, máy tính, điện thoại v.v.)
Khi các phụ huynh ngày càng có thêm nhiều đồ công nghệ, họ càng xa cách con cái. Thiếu vắng bố mẹ, trẻ con lại gắn với các thiết bị nhiều hơn, và điều này dẫn đến nghiện ngập. Cứ 11 trẻ độ tuổi 8 đến 18 lại có 1 trẻ bị nghiệm các thiết công nghệ.
9. Bức xạ từ máy móc
Tháng 5 năm 2011, Tổ chức sức khỏe Thế giới đã chính thức xếp điện thoại di động (và các thiết bị không dây khác) đứng thứ hai trong danh mục những thứ có nguy cơ tạo nên bức xạ từ máy móc. “Trẻ em nhạy cảm với các nhân tố tác động hơn người lớn vì bộ não của trẻ và hệ thống miễn dịch còn đang phát triển, vậy nên bạn không thể nói nguy cơ đối với người lớn và trẻ em là giống nhau được” (Globe and Mail 2011)
10. Không thể biện hộ được
Không thể biện hộ cho việc nuôi dạy và giáo dục trẻ bằng các thiết bị điện tử. Trẻ em là tương lai, nhưng không có tương lai tốt đẹp nào cho trẻ lạm dụng các thiết bị điện thử. Một phương pháp giải quyết vấn đề theo nhóm là cần thiết và cấp bách để giảm việc sử dụng thiết bị công nghệ ở trẻ hiện nay.
Hoài Phương
GỐC TIẾNG ANH:
10 Reasons Why Handheld Devices Should Be Banned for Children Under the Age of 12
Posted:
Updated:
Print Article
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Canadian Society of Pediatrics state infants aged 0-2 years should not have any exposure to technology, 3-5 years be restricted to one hour per day, and 6-18 years restricted to 2 hours per day (AAP 2001/13, CPS 2010). Children and youth use 4-5 times the recommended amount of technology, with serious and often life threatening consequences (Kaiser Foundation 2010, Active Healthy Kids Canada 2012). Handheld devices (cell phones, tablets, electronic games) have dramatically increased the accessibility and usage of technology, especially by very young children (Common Sense Media, 2013). As a pediatric occupational therapist, I'm calling on parents, teachers and governments to ban the use of all handheld devices for children under the age of 12 years. Following are 10 research-based reasons for this ban. Please visit zonein.ca to view the Zone'in Fact Sheet for referenced research.
1. Rapid brain growth
Between 0 and 2 years, infant's brains triple in size, and continue in a state of rapid development to 21 years of age (Christakis 2011). Early brain development is determined by environmental stimuli, or lack thereof. Stimulation to a developing brain caused by overexposure to technologies (cell phones, internet, iPads, TV), has been shown to be associated with executive functioning and attention deficit, cognitive delays, impaired learning, increased impulsivity and decreased ability to self-regulate, e.g. tantrums (Small 2008, Pagini 2010).
2. Delayed Development
Technology use restricts movement, which can result in delayed development. One in three children now enter school developmentally delayed, negatively impacting literacy and academic achievement (HELP EDI Maps 2013). Movement enhances attention and learning ability (Ratey 2008). Use of technology under the age of 12 years is detrimental to child development and learning (Rowan 2010).
3. Epidemic Obesity
TV and video game use correlates with increased obesity (Tremblay 2005). Children who are allowed a device in their bedrooms have 30% increased incidence of obesity (Feng 2011). One in four Canadian, and one in three U.S. children are obese (Tremblay 2011). 30% of children with obesity will develop diabetes, and obese individuals are at higher risk for early stroke and heart attack, gravely shortening life expectancy (Center for Disease Control and Prevention 2010). Largely due to obesity, 21st century children may be the first generation many of whom will not outlive their parents (Professor Andrew Prentice, BBC News 2002).
4. Sleep Deprivation
60% of parents do not supervise their child's technology usage, and 75% of children are allowed technology in their bedrooms (Kaiser Foundation 2010). 75% of children aged 9 and 10 years are sleep deprived to the extent that their grades are detrimentally impacted (Boston College 2012).
5. Mental Illness
Technology overuse is implicated as a causal factor in rising rates of child depression, anxiety, attachment disorder, attention deficit, autism, bipolar disorder, psychosis and problematic child behavior (Bristol University 2010, Mentzoni 2011, Shin 2011, Liberatore 2011, Robinson 2008). One in six Canadian children have a diagnosed mental illness, many of whom are on dangerous psychotropic medication (Waddell 2007).
6. Aggression
Violent media content can cause child aggression (Anderson, 2007). Young children are increasingly exposed to rising incidence of physical and sexual violence in today's media. "Grand Theft Auto V" portrays explicit sex, murder, rape, torture and mutilation, as do many movies and TV shows. The U.S. has categorized media violence as a Public Health Risk due to causal impact on child aggression (Huesmann 2007). Media reports increased use of restraints and seclusion rooms with children who exhibit uncontrolled aggression.
7. Digital dementia
High speed media content can contribute to attention deficit, as well as decreased concentration and memory, due to the brain pruning neuronal tracks to the frontal cortex (Christakis 2004, Small 2008). Children who can't pay attention can't learn.
8. Addictions
As parents attach more and more to technology, they are detaching from their children. In the absence of parental attachment, detached children can attach to devices, which can result in addiction (Rowan 2010). One in 11 children aged 8-18 years are addicted to technology (Gentile 2009).
9. Radiation emission
In May of 2011, the World Health Organization classified cell phones (and other wireless devices) as a category 2B risk (possible carcinogen) due to radiation emission (WHO 2011). James McNamee with Health Canada in October of 2011 issued a cautionary warning stating "Children are more sensitive to a variety of agents than adults as their brains and immune systems are still developing, so you can't say the risk would be equal for a small adult as for a child." (Globe and Mail 2011). In December, 2013 Dr. Anthony Miller from the University of Toronto's School of Public Health recommend that based on new research, radio frequency exposure should be reclassified as a 2A (probable carcinogen), not a 2B (possible carcinogen). American Academy of Pediatrics requested review of EMF radiation emissions from technology devices, citing three reasons regarding impact on children (AAP 2013).
10. Unsustainable
The ways in which children are raised and educated with technology are no longer sustainable (Rowan 2010). Children are our future, but there is no future for children who overuse technology. A team-based approach is necessary and urgent in order to reduce the use of technology by children. Please reference below slide shows on www.zonein.ca under "videos" to share with others who are concerned about technology overuse by children.
Problems - Suffer the Children - 4 minutes
Solutions - Balanced Technology Management - 7 minutes
The following Technology Use Guidelines for children and youth were developed by Cris Rowan, pediatric occupational therapist and author of Virtual Child; Dr. Andrew Doan, neuroscientist and author of Hooked on Games; and Dr. Hilarie Cash, Director of reSTART Internet Addiction Recovery Program and author of Video Games and Your Kids, with contribution from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Canadian Pediatric Society in an effort to ensure sustainable futures for all children.
Technology Use Guidelines for Children and Youth
Please contact Cris Rowan at info@zonein.ca for additional information. © Zone'in February

